There might be scenarios where you might want to export the data from Power BI to SQL server. In my case there were two dashboard where a certain value was not matching and i wanted to do a SQL query to figure out what was missing.
So with some research I found out that, Power BI uses SSAS services in the background to store and fetch data to and from the datamodel that is created. Power BI ships with the SSAS service "msmdsrv.exe" (found in bin folder of power bi installation) and an instance of this service is create for each power bi desktop session.
If we can access this instance we should also be able to import data from the same. We know that the service would be running on the localhost but what we dont know is the port at which it is running. To find the port number is a two step process:
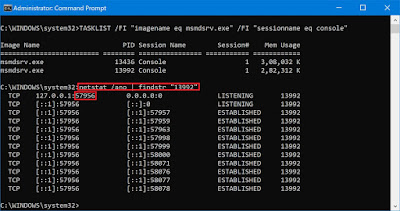
Step 1: Find the ProcessID of the msmdsve.exe on the local server use the following command on an elevated command prompt.
TASKLIST /FI "imagename eq msmdsrv.exe" /FI "sessionname eq console"
Now one needs to chose the PID and fetch the details of the process using the following command in an elevated command prompt:
netstat /ano | findstr "<PID from step 1>"
We have used PID 15480 from the first command and from the TCP responses the first line exposes the port number that is being used by the service.
Create a SSIS project in Visual Studio and drag the DataFlow task on the canvas as shown below.
Right click the data flow task and choose edit. This should take us to the DataFlow tab from the control flow tab. In the dataflow tab select Source assitance and create a new connection to the local SSAS server that we figured out in the steps above
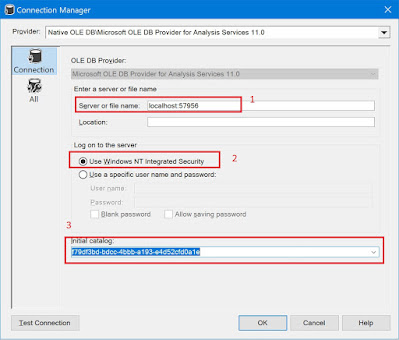
While creating the Connection make sure that you select the provider as OLE DB Provider for Analysis Server (as shown below).
Use the server name details as discovered with NT authentication and just select the intial catalogue whcih is randomly generated.
Now create a destination connection using the Destination assistant from the toolbar. Once the source and destination connections are created we will end us with a screen as shown below. We need to then connect the two tasks that are created.
Now, edit the source connection and populate the details similar to as show below.
The SSIS package can now be executed to import the data. One issue that I have noticed with the above procedure is that the data type for the different columns is not correctly identified and a lot of the columns end up being imported as varchar(255) an alternate to this could be to format this data in excel file and then import from excel after formatting the columns there.
To import the data into excel we need to create a connection to the SSAS server with the same details as above. The only trick that is required in this process is to treat the SSAS source as a table rather than a cube so that flat data can be imported.
When the connection to SSAS cube is created the connection is saved as a folder "C:\Users\santosh.singh\Documents\My Data Sources" (replace santosh.singh with the user name that you are logged in with).
In this folder locate the connection that you have just created and edit this as a text file replace the two fields (CommandType and CommandText)
Enter the CommandType as Query and CommandText with a DAX Query which to extact a flat table from a cube is evaluate <TableName>
Once the above changes are done import the data using Excel and the data would appear as a flat table rather than a cube (Pivot). Once the import is done format the columns with the correct data type and then import the excel into SQL server using SSIS.